NECO Biology Practical Questions and Answers. This article contains all the 2025 NECO biology specimens, questions and answers. Make sure that you don’t joke with any information in this particular post.
Are you a candidate of the 2025 NECO examination and you are going to write biology during the examination? I bring you this good news.
It is my pleasure to announce to you that the 2025 NECO biology practical specimens, questions and answers are out. If you are reading this article, it means that you are one of those lucky candidates who are going to see the solutions even before getting to the examination hall.
A lot of questions have been trending about how get the biology practical questions and answers. That is the reason why I have decided to release this EXPO here.
You should know that for every examination, practical carries the major mark. This means that if fail practical, you have impliedly failed the examination totally.
Therefore, if you would like to score an ‘A’ in the forthcoming NECO biology examination, you endeavor to study everything that I am going to reveal in this article.
Complete List of NECO Biology Specimen
The 2023 NECO biology specimens have been by the examination council. They include the following:
Specimen A: Cervical Vertebrae
Specimen B: Lumber Vertebrae
Specimen C: Rib bone
Specimen D: Guava fruit
Specimen E: Combretum
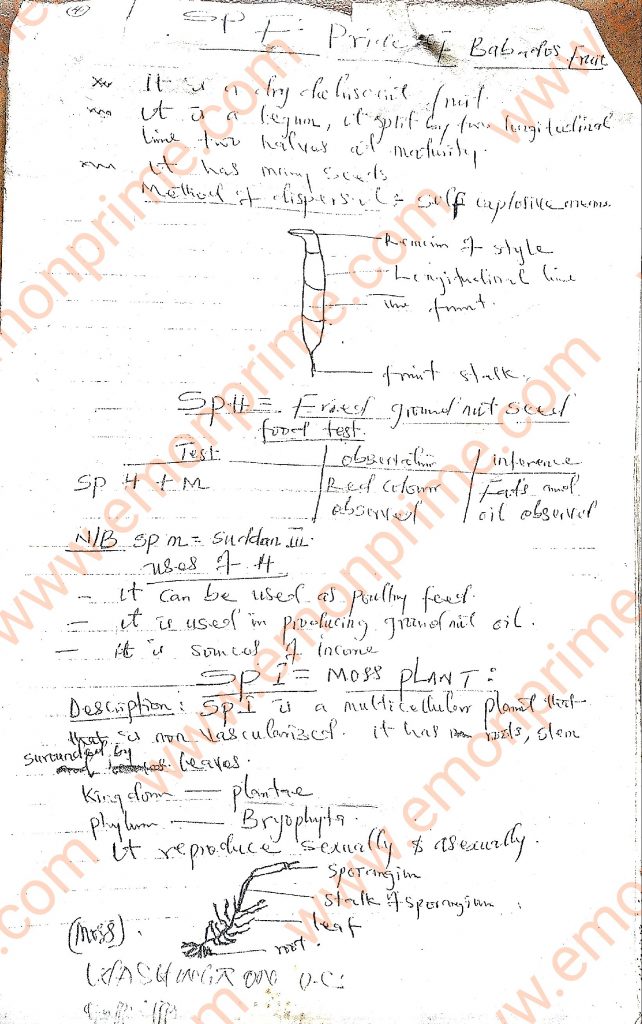
Specimen F: Pride of Barbados fruit
Specimen G: Bean Seed
Specimen H: Fried groundnut seed
Specimen I: Moss plant
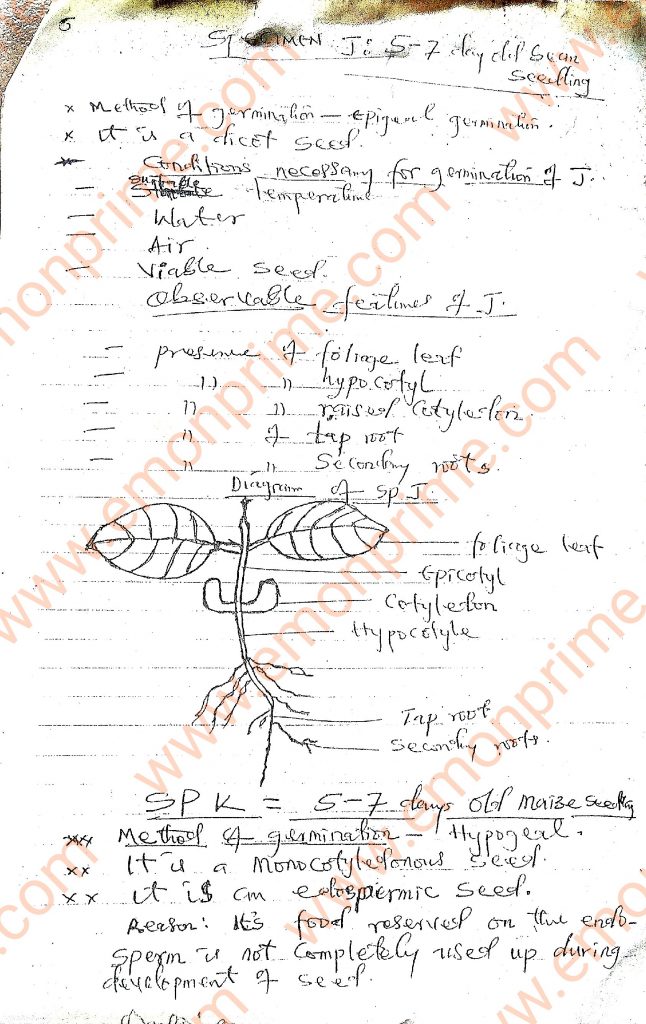
Specimen J: 5-7 day old bean seedling
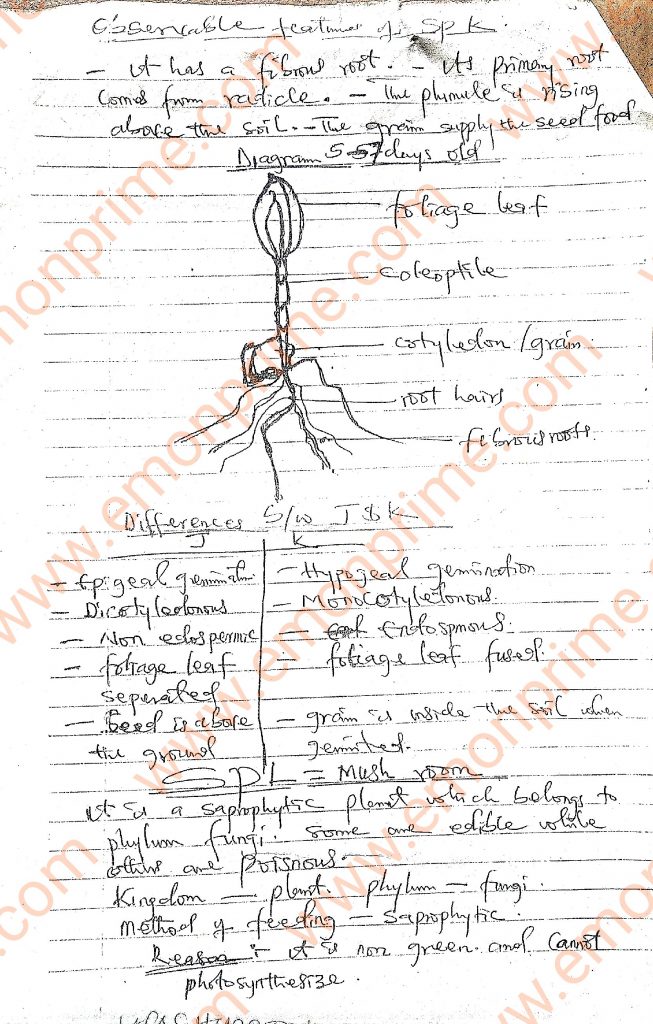
Specimen K: 5-7 day old maize seedling
Specimen L: Mushroom
Specimen N: Earthworm
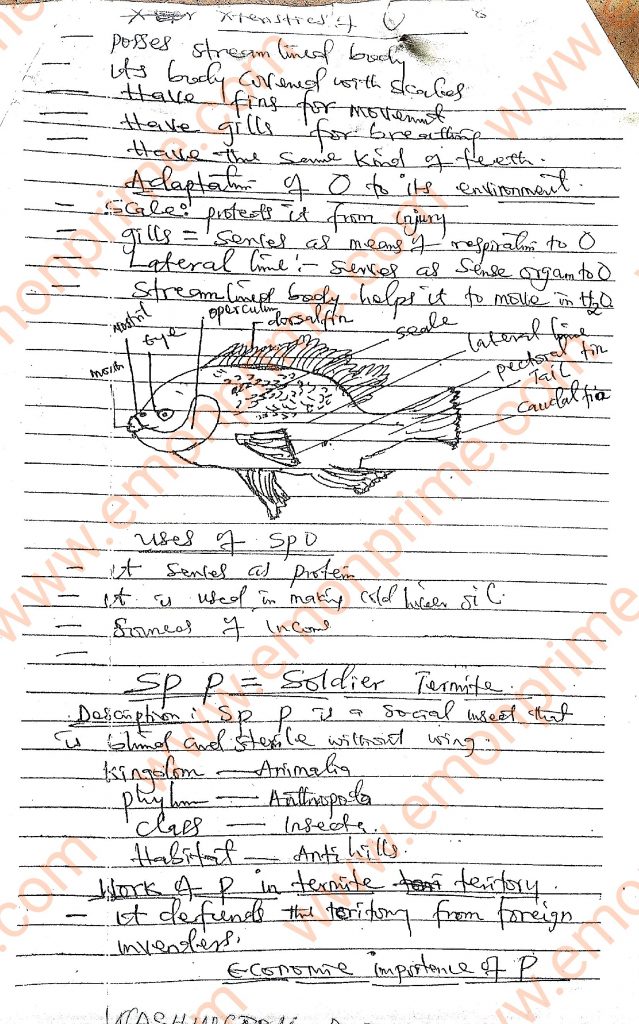
Specimen O: Tilapia
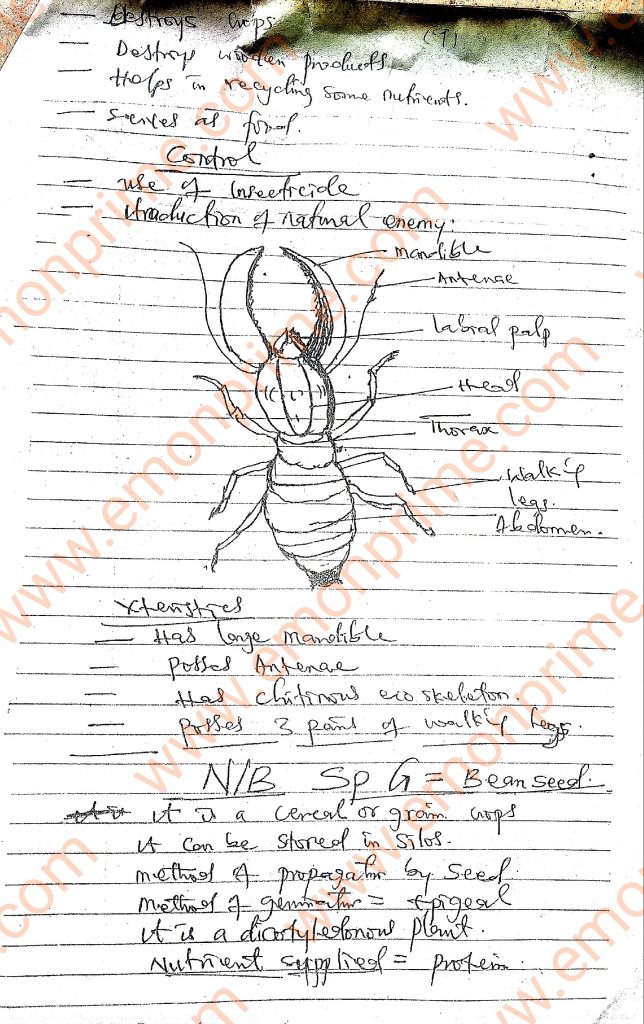
Specimen P: Soldier Termite
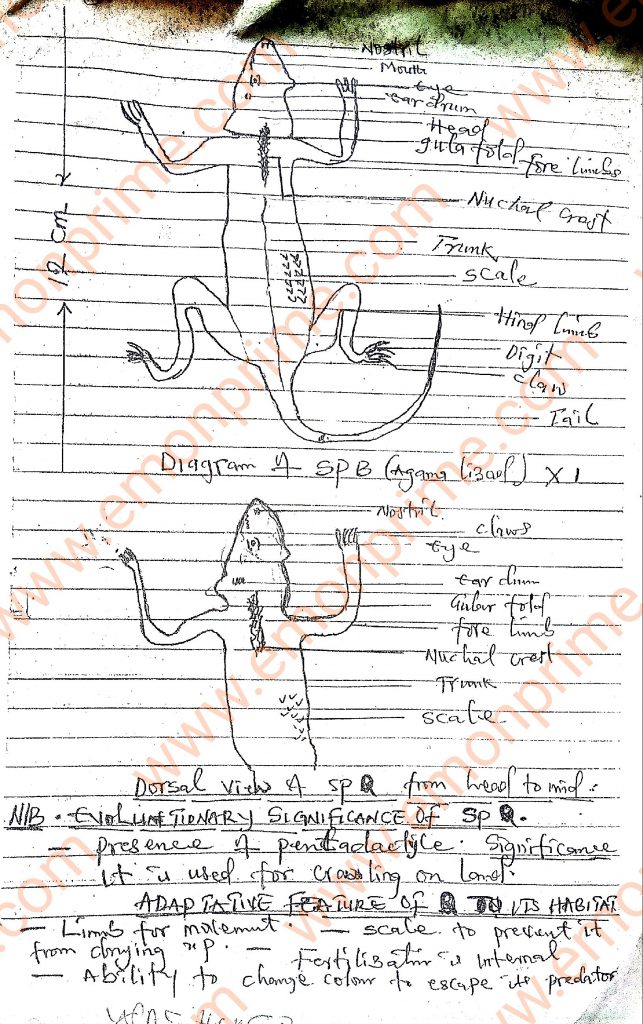
Specimen Q: Agama Lizard
Specimen R: Snail
Biology Specimen and Answers (Study Guide)



2025 NECO Biology Specimen (Newly Released)
These are the newly released 2023 biology specimen. Every school is expected to get them and teach their biology students who will be writing the examination.
Specimen A: Microscope
Specimen B: A Ripe Mango Fruit
Specimen C: Transverse Section of Tomato Fruit
Specimen D: Groundnut Seed (Fried/Dried)
Specimen E: Maize Grain
Specimen F: Carrot
Specimen G: Irish Potatoes (RAW)
Specimen H: Water Lily
Specimen I: Prawn
Specimen J: Tilapia Fish
Specimen K: Tadpole (8-9 weeks old)
Specimen L: Spider
See also: NECO Biology Questions and Answers for 2025 | Essay and Objectives
NECO Biology Practical Questions and Answers 2025
(1aii)
1. Eye piece lens
2. Objective lens
3. Stage
(1aiii)
Specimen A is used to study small organisms and cells in the laboratory
(1bi)
(1bii)
Specimen B is dispersed by animals
(1biii)
1. It is edible.
2. it is brightly colored
(1biv)
In a tabular form:
Specimen B:
1. One seeded
2. Hard and woody endocarp
Specimen C.
1. Many seeded.
2. Fleshy endocarp
(1ci)
In a tabular form:
Experiment:
Observation: Spot becomes translucent.
Conclusion: Oil is present.
(1cii)
Fats and oil is present in specimen D.
(1ciii)
1. Specimen E is a source of food for man.
(2ai)
Specimen F – Carrot
Specimen G – Irish Potato
Specimen H – Water lily
Specimen I – Prawn
(2aii)
Vitamin A in specimen F helps to maintain healthy eyes, teeth, skeletal and soft tissue, mucus membranes and skin.
(2aiii)
It has a swollen root
(2aiv)
In a tabular form:
Experiment.
Observation: G turns blue black in colour.
Conclusion: Starch is present.
(2bi)
1. Presence of long petiole which supports the broad lamina on the surface of the water.
2. The upper surface of the leaf is waxy which prevents the clogging of the stomata.
3. Presence of well-developed and numerous adventitious roots which anchors the plant firmly
4. Flowers are raised above water surface by long stalks for purpose of pollination.
(2bii)
Specimen I belongs to the class of Crustacea.
(2biii)
1. It has two body regions.
2. It has a pair of antennae.
(2biv)
In a tabular form:
External feature:
1. Pair of antennae
2. Pair of legs
3. Stalked compound eyes.
Function:
1. For feeling
2. For walking
3. For sight
(2bv)
(i) It serves as food for man
(ii) It serves a source of income
(3ai)
J-Tilapia fish
K-Tadpole
L-Spider.
(3bii)
1. Possession of laterally flattened and streamlined body for easy movement in water.
2. Possession of pectoral and pelvic fins for slow movement, balancing and steering.
(3ci)
1. Prosoma
2. Opisthosoma (or abdomen)
(3cii)
Specimen L belongs to the class Arachnida.
(3ciii)
1. It has eight walking legs
2. It has eight simple eyes.
Expected NECO Biology Practical Questions
The questions below are for practice, not the 2025 Biology Practical questions.
1. (a) (i) Phylum of specimens C/Butterfly and E/Grasshopper: Arthropoda
(ii) Reasons for the answer in 1 (a)(i): (I) Metameric segmentation/segmented bodies: (II) Jointed appendages; (III) presence of chitinous exoskeleton/exoskeleton made of chitin; (IV) Bilateral symmetry.
(b) differences between
(i)
| C/Butterfly | D/Caterpillar |
| Wings present | Wings are absent |
| Proboscis present | Mandibles are present |
| Proleg absent | Mandibles are present |
| Legs are longer | Legs are shorter |
| Claspers are absent | Claspers are present |
| Has one pair of compound eyes | Has simple eyes |
| Has antennae | Absence of antennae |
| Osmeterium absent | Osmeterium present |
(ii)
| C/Butterfly | E/Grasshopper |
| Presence of proboscis | Presence of mandibles |
| Clubbed/rounded/knobbed antennae | Not clubbed/rounded/knobbed antennae/tapering antennae; |
| Wing is membreneous/soft | Harder/less membraneous wings/forewings are leathery |
| Surface of wing is powdery/have scales/eye spots | Surface of wing is not powdery/absence of scales/eye spots; |
| Hind limbs/legs smaller/shorter/less muscular | Hind limbs/legs/larger and elongated/more muscular |
| Abdomen is hairy | Abdomen is not hairy/smooth |
(c) Relationship between specimens C/Butterfly and D/Caterpillar:
(i) C/butterfly is the adult/image of D/Caterpillar
(ii) D/Caterpillar is the larva/larva stage of C/Butterfly
(d) (i) Habitat of specimen D/Caterpillar: Garden/Citrus leaves/vegetables/leaves/fruits/green plant has three pairs of true legs with claws for locomotion. (III) it has claspers; for attachment to vegetation/twid; (IV) presence of four pairs of prologs/false legs: for climbing; (V) its coloured pattern; enables it to blend with its environment/camouflages/escape predators; (VI) it has spiracles; for gaseous exchange, (VII) it has simple eyes for vision (VIII) has osmeterium; as defense mechanism/which emits foul smell to scare away predators.
(e) Diagram/drawing of dorsal view of specimen C/Butterfly
2(a)observable features of biological importance in
Specimen F/Carrot: (i) Main root/tap root/swollen/root tuber; (ii) Presence of lateral roots; (iii) Presence of short stem (green) ; (iv) Presence of foliage leaves; (v) Part of main root tapering
Specimen G/Irish potato: (i) Swollen stem/stem tuber; (ii) Bud(s)/ eye; (iii) Lenticels; (iv) scale leaf; (v) adventitious roots(s)
(b) (i) Classification of (I) Specimen F/Carrot: Root tuber; (II) Specimen G/Irish Potato: Stem tuber. Stem (above the swollen tap root). Specimen G/Irish Potato: Swollen, Stem/tuber; presence of bud(s)/eye; presence of scale leaves/leaf; presence of lentice(s).
(c) Class of specimen H and J: insect
(d) (i) Observable differences between specimen H and J.
| H/Adult mosquito | J/Adult cockroach |
| Smaller in size | Big/large in size |
| A pair of wings | Two pairs of wings; |
| Absence of hard hind wing | Presence of hard hind wing/elytra; |
| Shorter antennae | Longer antennae |
| Proboscis | Mandible |
| Absence of maxillary palp/maxilla | Presence of maxillary palp/maxilla |
| Thin legs | Thick/large legs; |
| Absence of spines on legs | Presence of spine on legs. |
(ii) Similarities between specimens H/adult mosquito and J/adult cockroach:
(i) Presence of a pair of compound eyes
(II) Body is divided into three divisions/head, thorax and abdomen
(iii) three pairs of/six(walking) legs
(IV) presence of jointed appendages
(V) presence of a pair of membraneous wings
(VI) Presence of a pair of antenna
(VII) Both have exoskeleton made of chitin
(VIII) Segmented Body.
(i) Feeding Habit of Specimen H/adult mosquito: Piercing and sucking. Specimen J/adult cockroach: Biting and chewing
(ii) Observing features used for feeding in specimen J/adult cockroach: Mandible; maxillae; labrum
4. (a) (i) Phylum of Specimen R/Earthworm: Annelida
(ii) Reasons for the classification of Specimen R/Earthworm:
(I) Presence of metameric segmentation/segments are separated from each other (by septa
(II) They are bilaterally symmetrical
(II) Segments are separated from each other
(IV) Presence of chaetae
(V) Body is covered by thin collagen cuticle
(VI) body is long and cylindrical.
(iii) Habitat of Specimen R/Earthworm:
(I) Under decaying leaves
(II) Wet/moist soil
(III) In open savanna/savannah beneath tall grasses
(IV) In the forests in decaying tree-stumps.
(b) (i) Features of adaption of Specimen R/Earthworm:
(I) Bristle like Caetae/seatea; for locomotion
(II) Mosit skin; for gaseous exchange
(III) Pointed anterior; for burrowing into the soil
(IV) Slimy body; reduces friction during movements
(V) Citellum; for attachment during exchange of sperms/reproduction/secretes cocoon (in which it eggs are deposited).
(ii) Economic importance of Specimen R/Earthworm:
(I) it aerates the soil
(II) it enriches/improves soil fertility
(III) its secretions neutralize the acid soil
(IV) Used as bait for fishing
(V) As food for some birds.
(c) Diagram/Drawing of the dorsal view of Specimen R/Earthworm
(d) Type of fruit: Specimen S/unripe mango fruit – Drupe, Specimen T/tomato fruit – Berry.
(e) (i) Observable differences between Specimens S and T
| Specimen C/Unripe Mango Fruit | Specimen T/tomato Fruit |
| Green in colour | Red/Yellow in colour |
| One seeded | Many seeded |
| Stony/hard endocarp | Fleshy/Succulent/Soft endocarp |
| Fibrous mesocarp | Succulent mesocarp |
| Seed large | Seed(s) small; |
| Basal placentation | Axile placentation |
| Mesocarp and endocarp are fused | Mesocarp had endocarp are not fused |
(ii) Similarities between specimens S and T:
(I) Both have seeds
(II) both are fruits
(III) Both have three layers/epicarp/mesocarp/endocarp/pericarp/fruit wall
(IV) Coloured epicarp/pericarp
(V) Both have placenta
(VI) Both have thin epicarp
(VII) both have fleshy mesocarp.
If you have any questions about the NECO Biology Practical, kindly let us know in the comment box.
Important Links
NECO Mathematics Questions and Answers for 2025 | Theories & Objective
NECO Marketing Questions and Answers for 2025 | Essay and Objectives
NECO Civic Education Questions and Answers for 2025 | Essay and Objectives
NECO Government Questions and Answers for 2025 | Essay and Objectives
NECO History Questions and Answers for 2025 | Essay & Objectives
I believe that you have found this article helpful. If you have any other question about NECO Biology Practical Specimen Questions and Answers, kindly make use of the comment section below.
If like this article and you feel it will be helpful someone else, please do well to share it using the social media platforms below.

I love the it
Great