This is the authentic WAEC Biology Questions and Answers 2025.
If you wish to see the 2025 Complete WAEC Biology Questions and Answers before the start of the examination and before every other person, make sure that you do not skip this article.
One of the major problems that most West Africa Examination Council (WAEC) candidates do face that usually results to poor performance in the examination is lack of proper guides.
Once every WAEC candidate is properly guided as regards the examination, there is going to be a massive improvement in the rate at which candidates passes the WAEC examination.
A notable example of such proper guide during the preparation of WAEC examination is having access to the expected questions and answers before going to the examination hall.
In this article, I am going to give you the exact biology questions for the 2025 WAEC examination with their respective answers. In case you are one of those who are preparing for this examination and you would like to prepare ahead of other candidates, please do joke with any information contained in this article.
This article is a typical ‘EXPO’ to what you are going to see in the West Africa Examination Council (WAEC) 2025.
WAEC Biology Objectives 2025:
1-10: CCBBBBABAC
11-20: CCABDBAADD
21-30: BDADDABABA
31-40: ACCAACBCCD
41-50: BCBCADCBCA
Biology Objective Questions For 2025
1. Which of the following organelles is common to both plant and animal cells?
A. Cellulose cell wall
B. Chlorophyll
C. Cell membrane
D. Large vacuole
The diagrams below are illustrations of different sections of a particular fruit. Study them and answer questions 2 and 3.
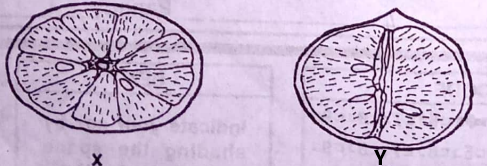
2. The sections in X and Y respectively, are
A. longitudinal and transverse
B. transverse and longitudinal
C. cross and transverse
D. transverse and cross
3. The fruit that has the illustrated sections is a
A. hesperidium
B. capsule
C. drupe
D. cypsela
The diagram below is an illustration of a fungus. Study it and answer questions 4 to 6.
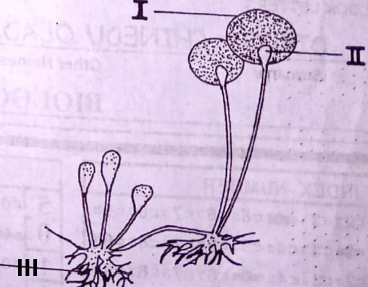
4. The structure labelled I is associated with
A. sexual reproduction
B. asexual reproduction
C. bud formation
D. gamete formation
5. The structure labelled II is the
A. spore
B. stolon
C. columella
D. sporangium
6. Which of the following statements about the structure labelled III is correct? It
A. secretes digestive enzymes into the substrate
B. absorbs mineral salts from the soil
C. forms the root hairs of the organism
D. develops into stolon
The diagram below is an illustration of a living organism. Study it and answer questions 7 and 8.
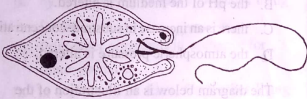
7. The level of organization of the organism is
A. tissue
B. cell
C. organ
D. system
8. The organism belongs to the Phylum
A. Rhizopoda
B. Ciliophora
C. Euglenophyta
D. Rhodophyta
9. A plant cell placed in a solution with a higher water potential will
A. expand and then shrink
B. enlarge and become turgid
C. expand and then burst
D. decrease in size and become flaccid
10. Offspring formed by sexual reproduction exhibit more variation than those formed by asexual reproduction because
A. greater amount of DNA is involved in sexual reproduction.
B. gametes of parents have different genetic composition.
C. genetic materials come from parents of two different species.
D. sexual reproduction is a lengthy process.
11. Radius and ulna are bones of the
A. pectoral girdle
B. upper arm
C. pelvic girdle
D. lower arm
12. The blood vessel which carries blood from the alimentary canal to the liver is the
A. hepatic artery
B. hepatic vein
C. hepatic portal vein
D. mesenteric artery
The diagram below is an illustration of the longitudinal section of a mammalian organ, Study it and answer questions 13 and 14.
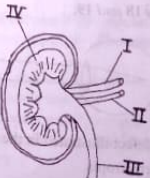
13. Which of the labelled parts is the cortex?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
14. What is the main function of the organ?
A. Excretion
B. Respiration
C. Reproduction
D. Locomotion
15. Detoxification of urea takes place in the
A. pancreas
B. heart
C. liver
D. testes
16. Which of the following hormones is suddenly secreted into the bloodstream of a frightened person?
A. Insulin
B. Adrenaline
C. Thyroxine
D. Parathormone
17. The temperature control centre in mammals is located in the
A. skin
B. hypothalamus
C. pituitary gland
D. adrenal gland
The diagram below is an illustration a type of eye defect in humans. Study it and answer questions 18 and 19.
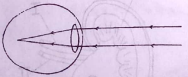
18. The eye defect illustrated in the diagram is
A. hypermetropia
B. astigmatism
C. presbyopia
D. myopia
19. The eye defect can be corrected by the use
A. convex lens
B. concave lens
C. bifocal lens
D. cylindrical lens
20. How many gametes are produced in the pollen grain of a flowering plant before fertilization?
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. Four
21. Which of the following organisms does not undergo incomplete metamorphosis?
A. Locust
B. Grasshopper
C. Butterfly
D. Cockroach
22. An enzyme reaction may begin to decline when
A. the optimum temperature is attained.
B. the pH of the medium is altered.
C. there is an increase in substrate concentration.
D. the atmospheric pressure is altered.
The diagram below is an illustration of the growth of a plant in a water culture. After a few days, the solution turned green and the plant died. Use it to answer questions 23 and 24.
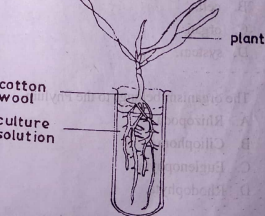
23. What precaution should have been taken to prevent the solution from turning green?
A. Use a non-green plant for the experiment
B. Aerate the solution daily
C. Cover the culture vessel with opaque paper
D. Keep cotton wool around the seedling to make it dry
24. The death of the plant was likely caused by
A. excess supply of nutrients to the plant
B. inadequate supply of water to the plant
C. algal growth in the solution that used up the nutrients
D. inability of the plant to make food due to lack of sunlight
25. Which of the following factors is not necessary for photosynthesis?
A. Water
B. Carbon (IV) oxide
C. Wind
D. Sunlight
26. Autotrophic nutrition is a process whereby an organism obtains food
A. by utilizing its stored energy
B. by synthesizing simple substances using energy
C. from other organisms in exchange for some products
D. in a synthesized form, from other living organisms
27. The process that takes place at the light stage of photosynthesis is
A. splitting of water molecules to form hydrogen ions
B. reduction of carbon (IV) oxide to form carbohydrate
C. formation of two molecules of phosphoglyceric acid
D. breaking down of ATP molecules to produce energy
28. The diagram below is an illustration of the foot of an animal.
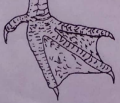
The adaptation of this type of foot is that it is
A. used as a bait to catch fish in water
B. used as a paddle for swimming
C. effective in scratching the soil for food
D. used for killing prey in water
29. The following organisms are examples of carnivorous plants except
A. Gloriosa
B. Venus flytrap
C. Pitcher plant
D. Utricularia
30. Plants and animals of an ecosystem make up a
A. habitat
B. succession
C. community
D. population
31. Rabbits cannot survive in an aquatic habitat because they have
A. no scales
B. no gills
C. fore limbs
D. lateral line
32. The illustration below is a food chain.
Grass → grasshopper → domestic fowl →hawk
What would happen if the population of domestic fowl decreases? The population of
A. grasshoppers would decrease
B. hawks would increase
C. grasshoppers would increase
D. grasses available to grasshoppers would increase
33. Which of the following features is a characteristic of aquatic plants? Possession of
A. multiple epidermis
B. heavily lignified tissue
C. finely divided leaves
D. succulent stem
34. An association between living organisms in which one organism lives on and feeds at the expense of the other organism is known as
A. mutualism
B. commensalism
C. parasitism
D. predation
35. When a large number of organisms share limited resources, the result is a
A. mutualism
B. extinction
C. commensalism
D. competition
36. Which of the following behaviours is correctly matched with the corresponding diseases?
| Behaviour | Diseases | |
| A | Smoking cigarette | Liver cirrhosis, lung cancer, AIDS |
| B | Having multiple sexual partners | Liver cirrhosis, syphilis, AIDS |
| C | Living near dirty- gutter | Lung cancer, syphilis, river blindness |
| D | Eating uncooked meat | Dysentery, cholera, food poisoning |
37. Endangered species are organisms that are
A. likely to migrate to other favourable lands
B. likely to disappear from the surface of the earth
C. reproducing profusely in an area
D. dangerous to humans and attacking other to animals
38. Which of the following practices is a wildlife conservation method?
A. Use of cover crops
B. Crop rotation
C. Mulching
D. Discouraging poaching
39. Which of the following resources cannot be conserved?
A. Forest
B. Water
C. Soil
D. Garbage
The diagrams below are illustrations of types of comb found in domestic fowl. Study them and answer questions 40 and 41.
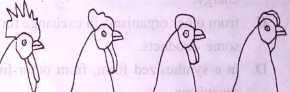
40. The types of comb show
A. variation
B. inheritance
C. cell theory
D. courtship behaviour
41. Which factor is most likely responsible for the various types of comb?
A. Environment
B. Genetics
C. Physiology
D. Morphology
42. Which of the following statements about mitosis is not correct?
A. Chiasmata are not formed
B. Bi-valents are not formed
C. It does not lead to variation
D. Four daughter cells are produced
43. A mixture of blood with antigen A and blood containing antibody a will
A. lead to agglutination
B. facilitate dissolution of clot
C. have no effect on blood composition
D. change the blood group
44. Plants suitable for experiments in genetics must not
A. produce numerous seeds within a short time
B. have a small number of chromosomes
C. have a relatively short life cycle
D. produce one generation in a long period
45. Which of the following statements about sickle cell anaemia is correct?
A. It is caused by sex-linked genes
B. It is more common in males than in females
C. Two sickle cell carrier parents may have a sickling child
D. It is caused by recessive genes
46. In humans, pointed eyebrows (B) is a dominant trait over smooth eyebrows (b). A student and the mother have smooth eyebrows while the father has pointed eyebrows. What is the genotype of the father?
A. BB
B. Bb
C. bb
D. BBbb
47. A woman with Rhesus negative blood group was advised not to marry a man with Rhesus positive blood group because
A. it will hinder her from having blood transfusion from her husband.
B. it will result in sickness and probably death of the offspring.
C. her children may all resemble her husband.
D. it may affect her childbearing ability.
48. Which of the following organisms exhibits division of labour?
A. Butterfly
B. Cockroach
C. Termite
D. Housefly
49. Natural selection arises as a result of
A. gene mutation
B. change of habitat
C. reduction in population
D. climate change
50. Which of the following statements is not Lamarck’s postulate on evolution?
A. Great changes in the environment result in corresponding changes in species
B. Frequently used organs become well developed while the ones not used become vestigial
C. Well-developed acquired characters are inheritable
D. Survivors in a competitive community must have inherited useful traits
See also: How to Pass WAEC Examination at One Sitting
Answers To Biology Objective Questions for 2025
I know that some people might be finding it difficult to answer the questions in the previuos section. That is the reason why I have decided to provide you with the answers to the objective questions.
The following are the correct answers to the biology objective questions for 2025 WAEC examination.
- C. Cell membrane
- B. transverse and longitudinal
- A. hesperidium
- B. asexual reproduction
- D. sporangium
- A. secretes digestive enzymes into the substrate
- B. cell
- C. Euglenophyta
- B. enlarge and become turgid
- B. gametes of parents have different genetic composition.
- B. upper arm
- C. hepatic portal vein
- D. IV
- A. Excretion
- C. liver
- B. Adrenaline
- B. hypothalamus
- A. hypermetropia
- A. convex lens
- B. Two
- C. Butterfly
- C. there is an increase in substrate concentration.
- C. Cover the culture vessel with opaque paper
- D. inability of the plant to make food due to lack of sunlight
- C. Wind
- B. by synthesizing simple substances using energy
- A. splitting of water molecules to form hydrogen ions
- B. used as a paddle for swimming
- A. Gloriosa
- C. community
- B. no gills
- C. grasshoppers would increase
- A. multiple epidermis
- C. parasitism
- D. competition
- B
- B. likely to disappear from the surface of the earth
- D. Discouraging poaching
- D. Garbage
- A. variation
- A. Environment
- D. Four daughter cells are produced
- A. lead to agglutination
- D. produce one generation in a long period
- D. It is caused by recessive genes
- B. Bb
- B. it will result in sickness and probably death of the offspring.
- C. Termite
- D. climate change
- D. Survivors in a competitive community must have inherited useful traits
WAEC Biology Theory Questions For 2025
The following questions are what you are likely going to see in the section two (theory) of the biology for 2025 WAEC examination.
1. (a) Describe briefly the role of the stomach in digestion.
(b) (i) Name three parts of plants in which food can be stored
(ii) Give one example in each case.
(c) Explain briefly how the level of sugar in the mammalian blood can be regulated.
1. (a)(i) What is sexual reproduction?
(ii) Name four organs in mammals that produce sex hormones.
(iii) Name one sex hormone produced by each of the organs named in
2(a)(i).
(b) In a tabular form outline three differences between reproductions in lizards and birds.
(c) (i) How are identical twins forms in humans?
(ii) State three characteristics features of identical twins.
1. (a) Explain the following terms:
(i) disease;
(ii) symptoms of diseases
(b) (i) List two physical and two chemical barriers that prevent pathogens from penetrating the body of an organism.
(ii) Explain how vaccination protects the body from contracting infectious diseases.
(c) Distinguish between an antibody and an antigen.
(d) Name the causative agents of: (i) Malaria; (ii) Cholera; (iii) AIDS.
1. (i) What is respiration?
(ii) In a tabular form, state four differences between gaseous exchange and aerobic respiration
(b) (i) Explain the term residual air.
(ii) What is the importance of residual air to mammals?
(iii) State four characteristic features associated with respiratory structures.
(c) (i) What is oxygen debt?
(ii) Outline three activities that can result in oxygen debt.
- (a) (i) What is conservation?
(ii) State six factors responsible for the decline of the abundance and variety of wildlife.
(b) Outline six ways in which the government can improve the situation in 5(a) (ii) above.
(c) (i) What is Eutrophication?
(ii) State two causes of eutrophication.
- (a) What is photosynthesis?
List: (i) four external factors;
(ii) two internal factors; that affect the rate of photosynthesis.
(b) (i) List the major products of the light dependent stage of photosynthesis.
(ii) State the importance of each of the products listed in 6(c) (i) above.
(c) (i) Explain why there are no green plants at the lower depths of some lakes.
(ii) State why decomposers are important to flowering plants.
- (a) (i) What is a gene?
(ii) Differentiate between the terms genotype and phenotype.
(b) Explain the following terms: (i) hybrid; (ii) pure breeding; (iii) nucleotide.
(c) In garden pea seeds, smooth seed coat is dominant over rough seed coat.
With the aid of a genetic diagram, determine the result expected if a homozygous rough pea is crossed with a smooth seed coat plant
Whose parent was rough coated?
- (a) (i) Describe epigeal germination of a seed.
(ii) In a tabular form, state three differences between epigeal germination and hypogeal germination.
(b) (i) What is seed dormancy?
(ii) State three ways by which dormancy in seeds can be broken.
(c) State six advantages of using contraceptives in human populations.
See also: How to Check Your WAEC Result Online
Related Posts
WAEC English Questions And Answers 2025 | Objectives, Test Of Orals and Essay
WAEC Economics Questions And Answers 2025 | Theories And Objectives
WAEC French Questions And Answers 2025 | Theories And Objectives
WAEC Mathematics Questions And Answers 2025 | Theory And Objectives
WAEC Physics Practical For 2025 | Specimens/Apparatus, Questions And Answers
WAEC Chemistry Questions And Answers For 2025 | Objectives And Theories
WAEC Biology Practical Specimen | Questions And Answers
Complete WAEC Physics Questions And Answers For 2025 (Objectives & Theory)
I believe that you found the information contained in this article very helpful. Always come to this site for more questions and answers for other WAEC subjects.
For any question about Complete WAEC Biology Questions and Answers for 2025, kindly make use of the comment section below.
Please share this information to others using any of the social media platforms shown below.

The theory answers are not here why